🧮 Math#
#bs.math:help
The beatifull world of mathematics… in Minecraft!
“Mathematics has very subtle inventions that can be of great service, both to satisfy the curious and to facilitate all arts and reduce the labor of men.”
—René Descartes
🔧 Functions#
You can find below all functions available in this module.
Combine#
- #bs.math:combine
Compute the combine of 2 numbers.
- Inputs:
Scores
$math.combine.[m,n] bs.in: Numbers to be combined, the smaller input will be taken from the greater input.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.combine bs.out: Result of the operation.
Technical limitation
The value of bs.out is incorrect if the result is greater than 2147483647 or $math.combine.[m,n] bs.in are not both positive.
Compute \(combine(4,2)\):
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.combine.m bs.in 4
scoreboard players set $math.combine.n bs.in 2
function #bs.math:combine
tellraw @a [{"text": "combine(4,2) = ","color":"dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.combine","objective":"bs.out"},"color":"gold"}]
Credits: Ethanout
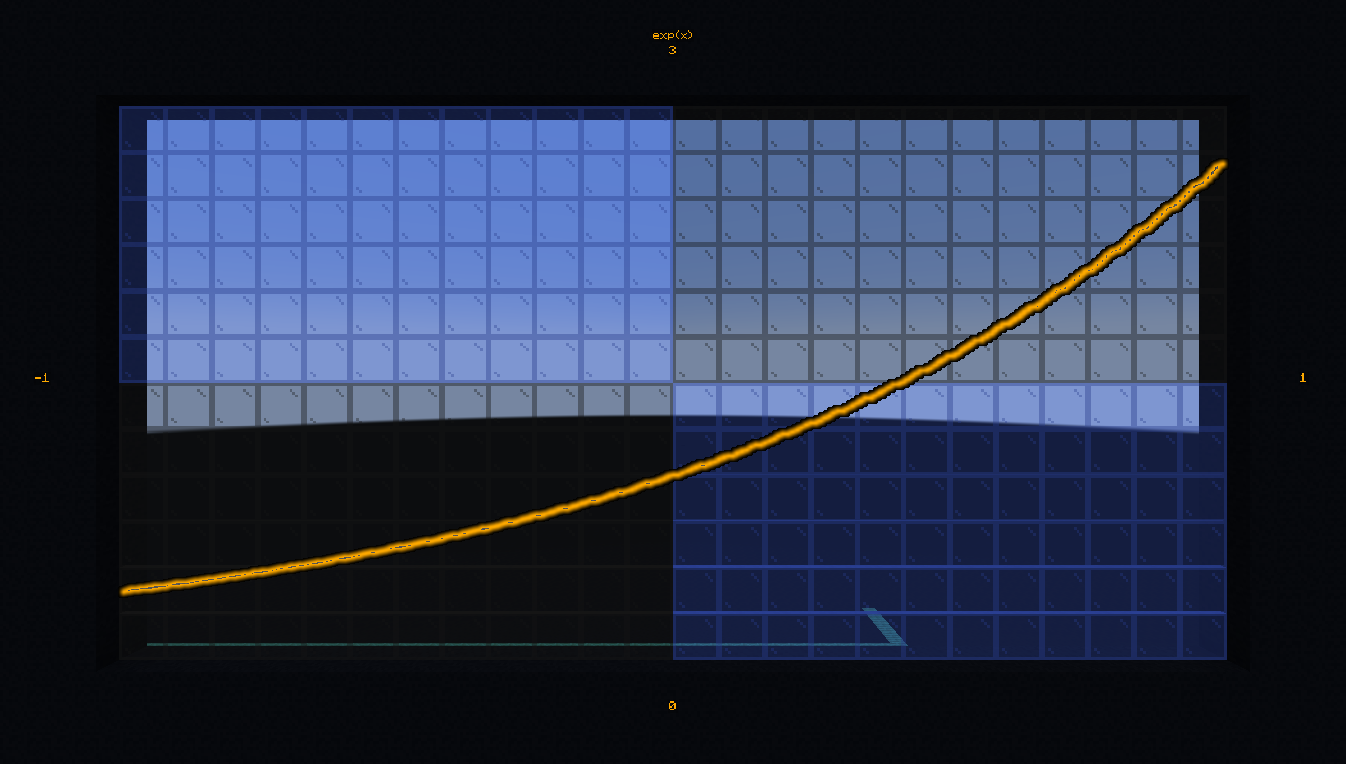
Exponential#
- #bs.math:exp
Compute the exponential function.
- Inputs:
Storage
bs:in math.exp.value[number]: Number to be exponentiated.- Outputs:
Storage
bs:out math.exp[double]: Result of the operation.
Technical limitation
Due to the limit of integers that can be stored in a score, the interval of bs:in is limited to [-6,15[.
Compute \(exp(3)\):
# Once
data modify storage bs:in math.exp.value set value 3.0
function #bs.math:exp
data get storage bs:out math.exp
Credits: Aksiome, KubbyDev
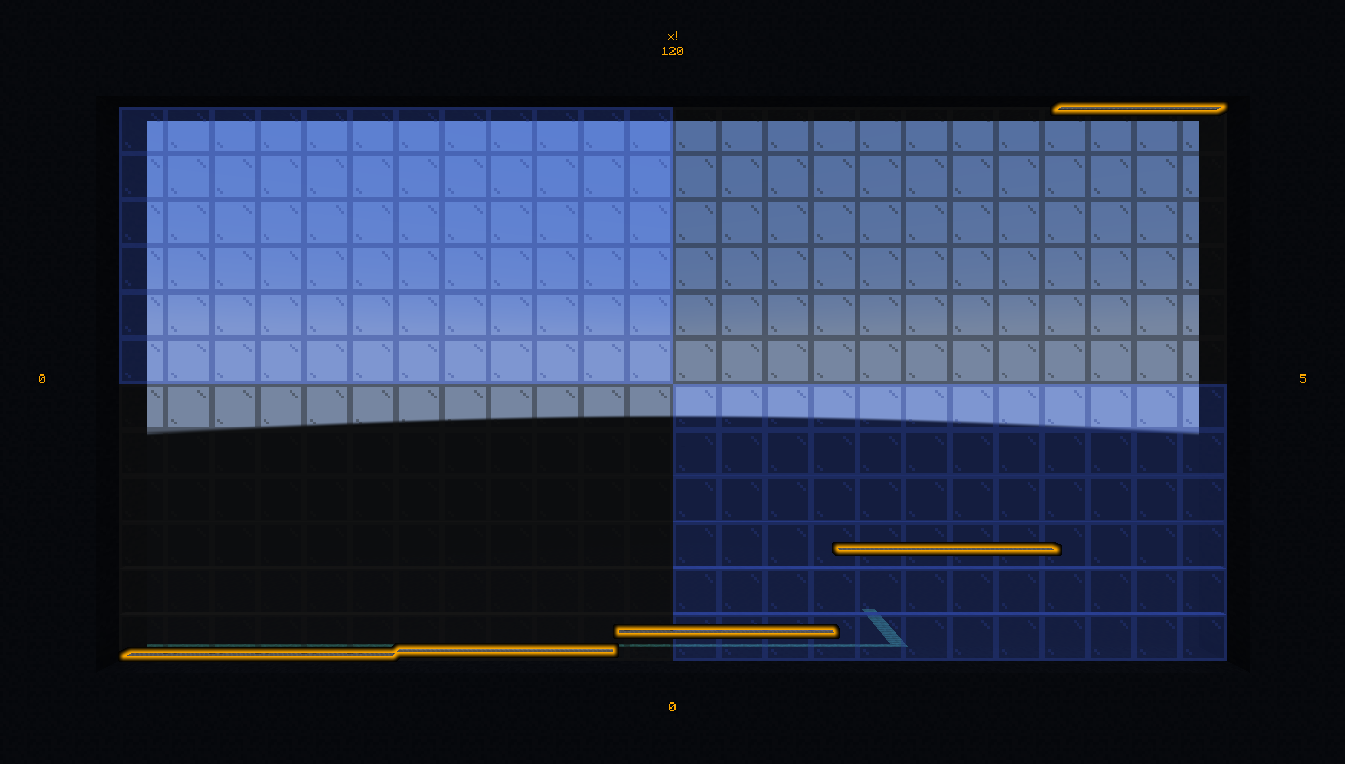
Factorial#
- #bs.math:factorial
Compute the factorial of the number.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.factorial.n bs.in: Number to be factorialized.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.factorial bs.out: Result of the operation.
Technical limitation
Due to the limit of integers that can be stored in a score, the interval of bs.in.0 is limited to [0,12].
Compute \(3!\):
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.factorial.n bs.in 3
function #bs.math:factorial
tellraw @a [{"text": "3! = ","color":"dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.factorial","objective":"bs.out"},"color":"gold"}]
Credits: KubbyDev
Float radix#
- #bs.math:frexp
Decompose a floating point number into a normalized fraction and an integral power of two.
- Inputs:
Storage
bs:in math.frexp.value[number]: Number to be decomposed.- Outputs:
Storage
bs:out math.frexp.e[int]: Exponent for the power of 2.Storage
bs:out math.frexp.x[double]: Normalized fraction in range]-1,-0.5]or[0.5,1[.
Decompose 5.8 into its mantissa and exponent:
# Once
data modify storage bs:in math.frexp.value set value 5.8
function #bs.math:frexp
data get storage bs:out math.frexp
Credits: Aksiome
Greatest common denominator#
- #bs.math:gcd
Compute the greatest common denominator of two numbers.
- Inputs:
Scores
$math.gcd.[a,b] bs.in: The two numbers.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.gcd bs.out: The greatest common denominator.
Calculate the greatest common denominator between 16 and 12:
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.gcd.a bs.in 16
scoreboard players set $math.gcd.b bs.in 12
function #bs.math:gcd
tellraw @a [{"text": "gcd(16,12) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.gcd", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
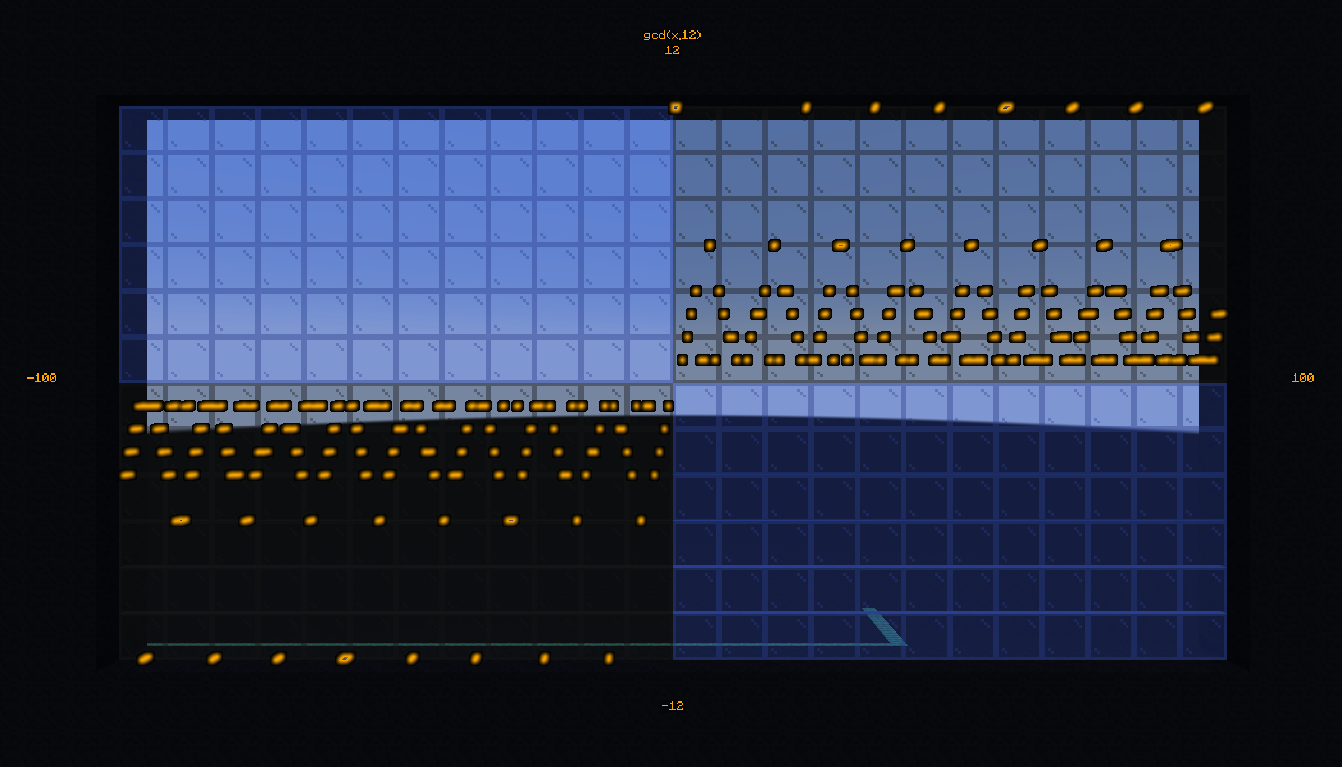
Credits: Aksiome, Leirof
Inverse trigonometry#
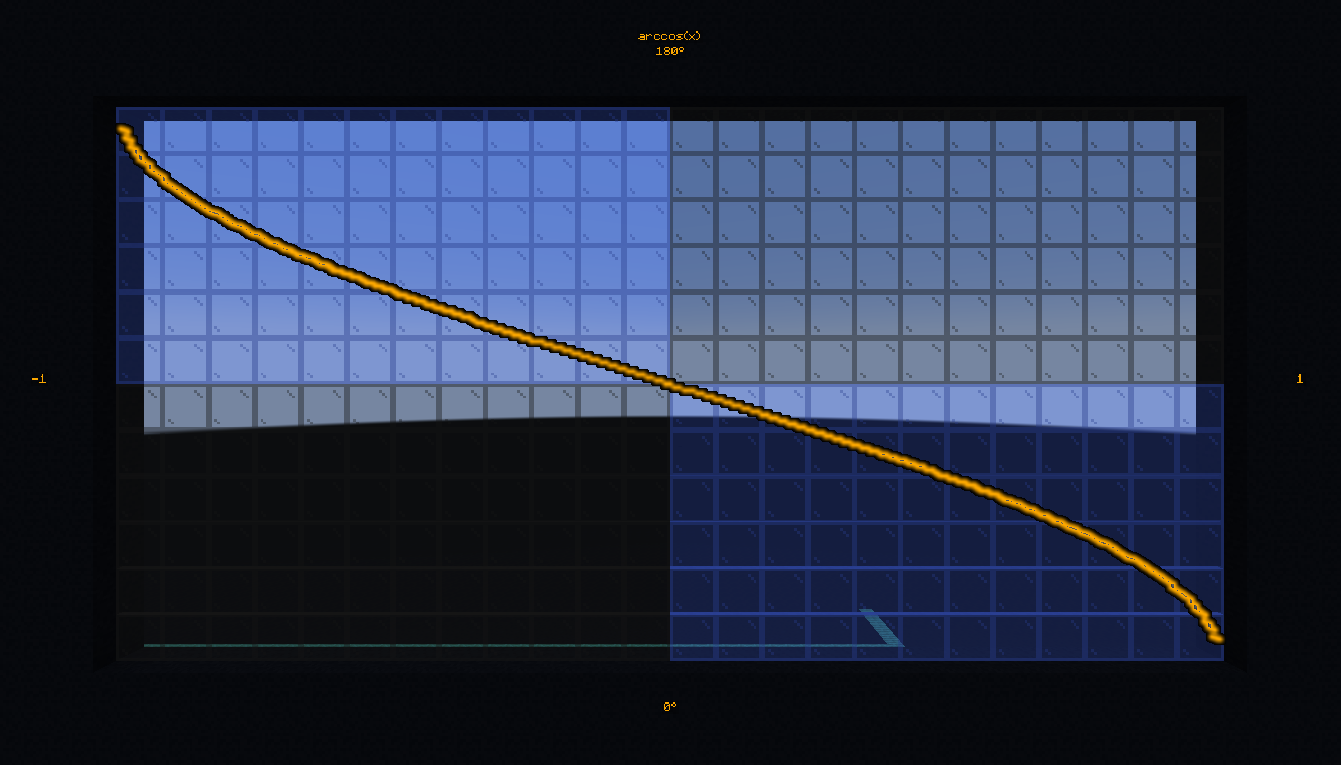
- #bs.math:acos
Compute the arc cosine of a value between -1 and 1.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.acos.value bs.in: Value you want to compute the arccosine of, shifted by 3 digits (1,2345 -> 1234) for better precision in integer scores.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.acos bs.out: Result of the operation in degrees, shifted by 2 digits.
Compute and display the arccosine of 0.42:
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.acos.value bs.in 420
function #bs.math:acos
tellraw @a [{"text":"acos(0.42) = ","color":"dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.acos","objective":"bs.out"},"color":"gold"}]
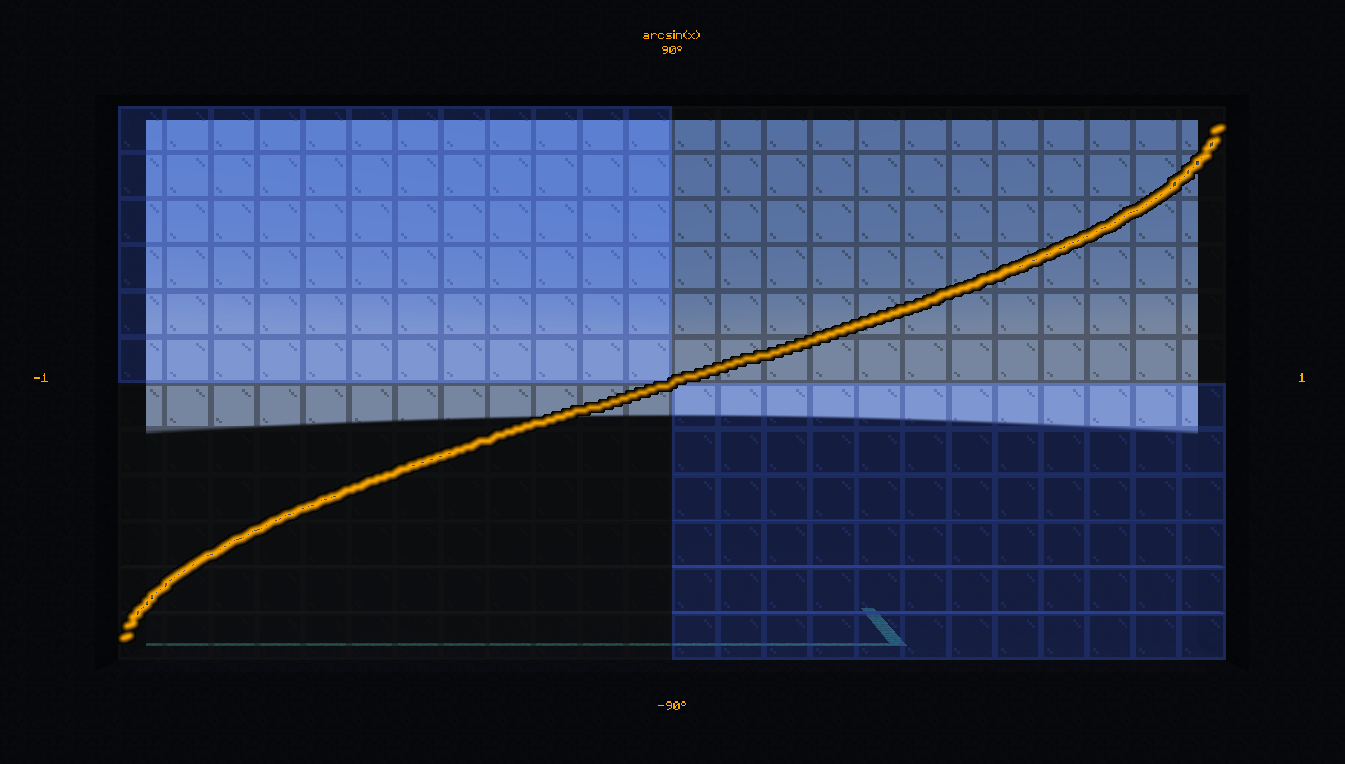
- #bs.math:asin
Compute the arc sine of a value between -1 and 1.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.asin.value bs.in: Value you want to compute the arcsine of, shifted by 3 digits (1,2345 -> 1234) for better precision in integer scores.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.asin bs.out: Result of the operation in degrees, shifted by 2 digits.
Compute and display the arcsine of 0.42:
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.asin.value bs.in 420
function #bs.math:asin
tellraw @a [{"text":"asin(0.42) = ","color":"dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.asin","objective":"bs.out"},"color":"gold"}]
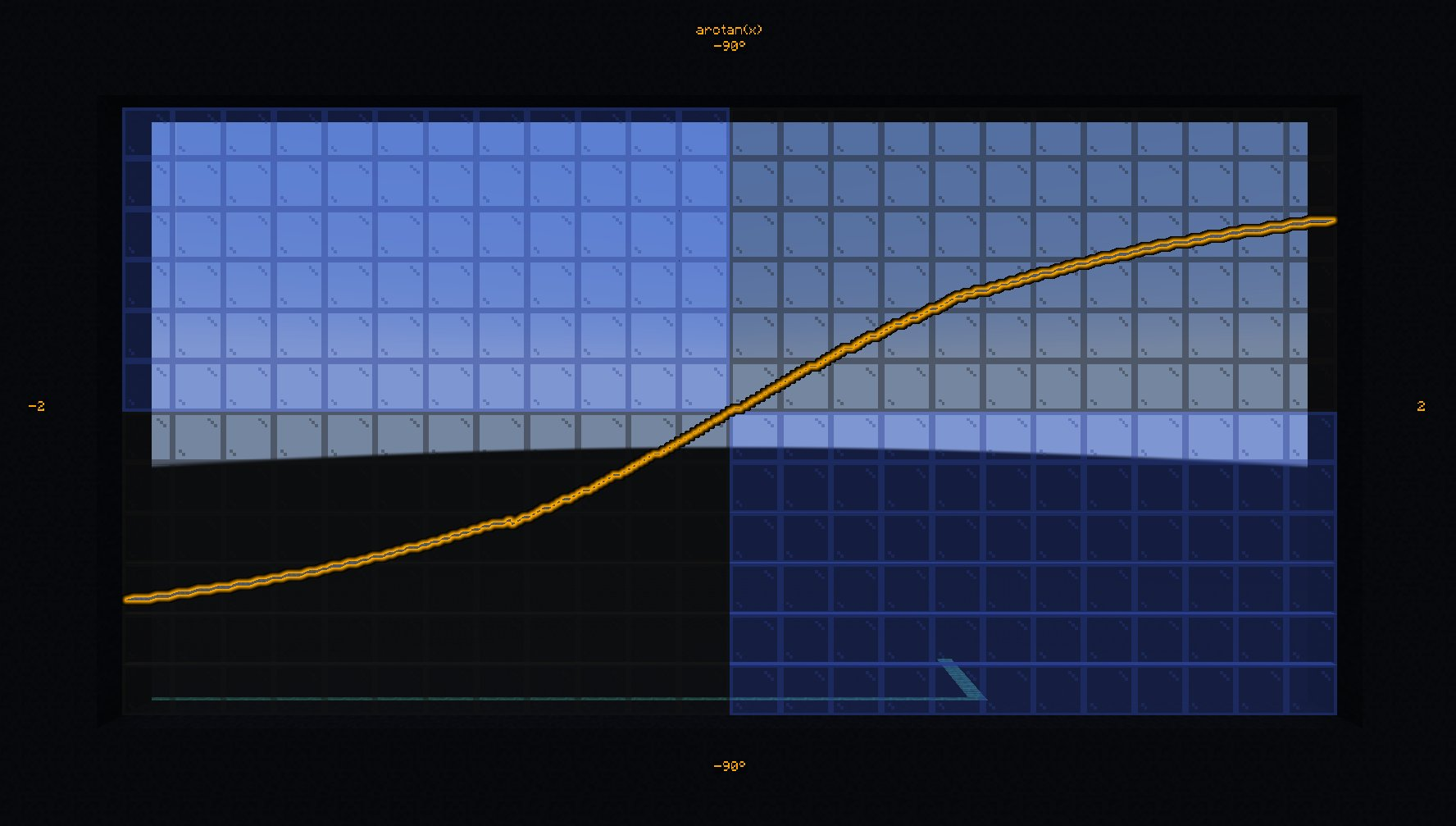
- #bs.math:atan
Compute the arc tangent of a value between -infinite and +infinite.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.atan.value bs.in: Value you want to compute the arctangent of, shifted by 3 digits (1,2345 -> 1234) for better precision in integer scores.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.atan bs.out: Result of the operation in degrees, shifted by 2 digits.
Compute and display the arctan of 0.42:
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.atan.value bs.in 420
function #bs.math:atan
tellraw @a [{"text":"atan(0.42) = ","color":"dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.atan","objective":"bs.out"},"color":"gold"}]
- #bs.math:atan2
Compute the 2-argument arctangent of y and x.
- Inputs:
Scores
$math.atan2.[y,x] bs.in: Values you want to compute the arctangent of, shifted by 3 digits (1,2345 -> 1234) for better precision in integer scores.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.atan2 bs.out: Result of the operation in degrees, shifted by 2 digits.
Compute and display the atan2 of (0.42, 0.8):
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.atan2.y bs.in 420
scoreboard players set $math.atan2.x bs.in 800
function #bs.math:atan2
tellraw @a [{"text":"atan2(0.42, 0.8) = ","color":"dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.atan2","objective":"bs.out"},"color":"gold"}]
Credits: Aksiome, KubbyDev, Leirof
Logarithm#
- #bs.math:log
Compute the Neperian logarithm (base e) of a number.
- Inputs:
Storage
bs:in math.log.value[number]: Number to be logarithmized.- Outputs:
Storage
bs:out math.log[double]: Result of the operation.
Calculate \(ln(28)\):
# Once
data modify storage bs:in math.log.value set value 28.0
function #bs.math:log
data get storage bs:out math.log
- #bs.math:log2
Compute the logarithm in base 2 of a number.
- Inputs:
Storage
bs:in math.log2.value[number]: Number to be logarithmized.- Outputs:
Storage
bs:out math.log2[double]: Result of the operation.
Calculate \(log_2(28)\):
# Once
data modify storage bs:in math.log2.value set value 28.0
function #bs.math:log2
data get storage bs:out math.log2
- #bs.math:log10
Compute the logarithm in base 10 of a number.
- Inputs:
Storage
bs:in math.log10.value[number]: Number to be logarithmized.- Outputs:
Storage
bs:out math.log10[double]: Result of the operation.
Calculate \(log_{10}(28)\):
# Once
data modify storage bs:in math.log10.value set value 28.0
function #bs.math:log10
data get storage bs:out math.log10
- #bs.math:loga
Compute the logarithm in base a of a number.
- Inputs:
Storage
bs:in math.loga.value[number]: Number to be logarithmized.Storage
bs:in math.loga.a[number]: Base of the logarithm.- Outputs:
Storage
bs:out math.loga[double]: Result of the operation.
Calculate \(log_4(28)\):
# Once
data modify storage bs:in math.loga.a set value 4
data modify storage bs:in math.loga.value set value 28.0
function #bs.math:loga
data get storage bs:out math.loga
Credits: Aksiome, KubbyDev
Power#
- #bs.math:pow {scaling:<scaling>}
Compute \(x^y\).
- Inputs:
Score
$math.pow.base bs.in: The base.Score
$math.pow.exp bs.in: The exponent.Macro Var
scaling[number]: Scalar for the function’s input base and the output.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.pow bs.out: Result of the operation.
Compute \(2.245^6\):
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.pow.base bs.in 2245
scoreboard players set $math.pow.exp bs.in 6
function #bs.math:pow {scale:1000}
tellraw @a [{"text": "(2.245^6)*(1000) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.pow", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
- #bs.math:pow2
Compute \(2^n\).
- Inputs:
Score
$math.pow2.exp bs.in: The exponent.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.pow2 bs.out: Result of the operation.
Compute \(2^6\):
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.pow2.exp bs.in 6
function #bs.math:pow2
tellraw @a [{"text": "2^6 = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.pow2", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
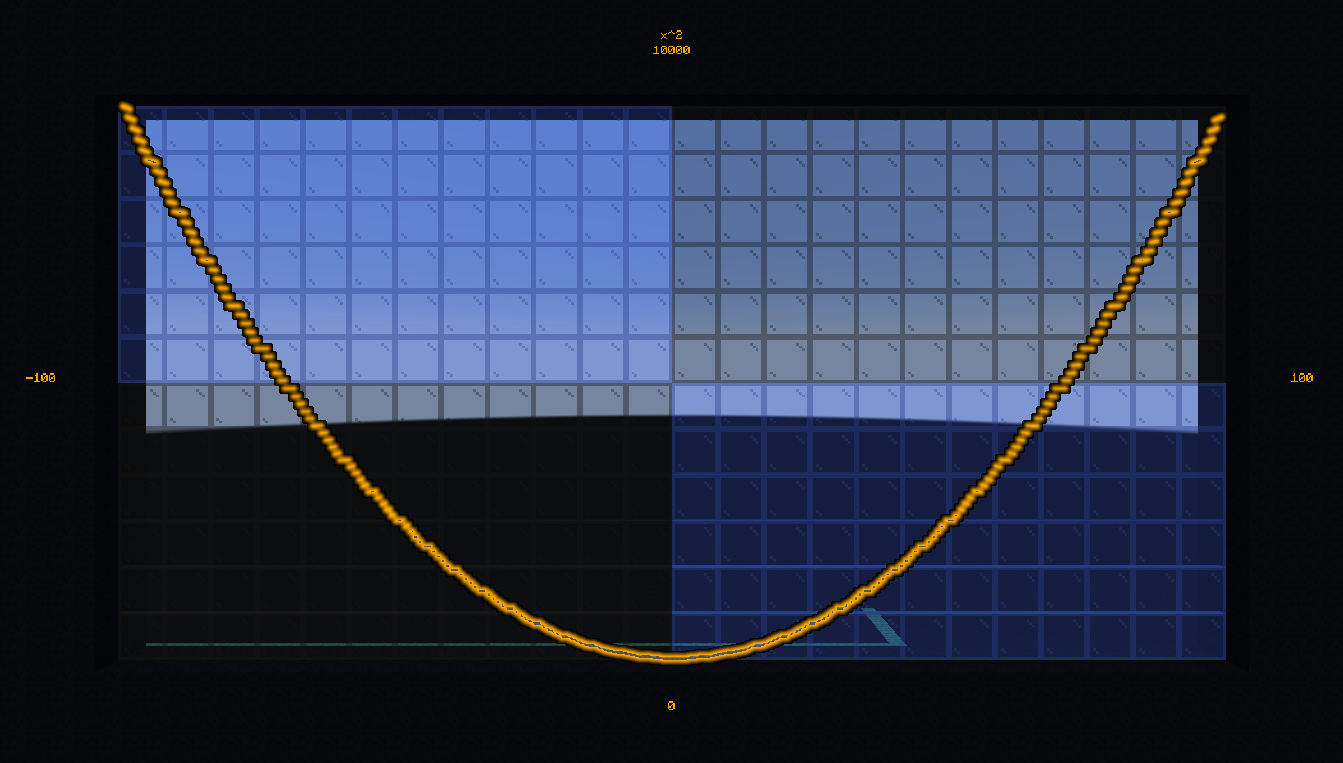
Credits: Aksiome, Leirof
Rounded division#
- #bs.math:divide
Divide a number by another then round the result to the nearest integer (Minecraft rounds down to the next integer).
- Inputs:
Score
$math.divide.num bs.in: The numerator.Score
$math.divide.den bs.in: The denominator.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.divide bs.out: Result of the division.
Calculate \(9/5\):
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.divide.num bs.in 9
scoreboard players set $math.divide.den bs.in 5
function #bs.math:divide
tellraw @a [{"text": "9 / 5 = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.divide", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
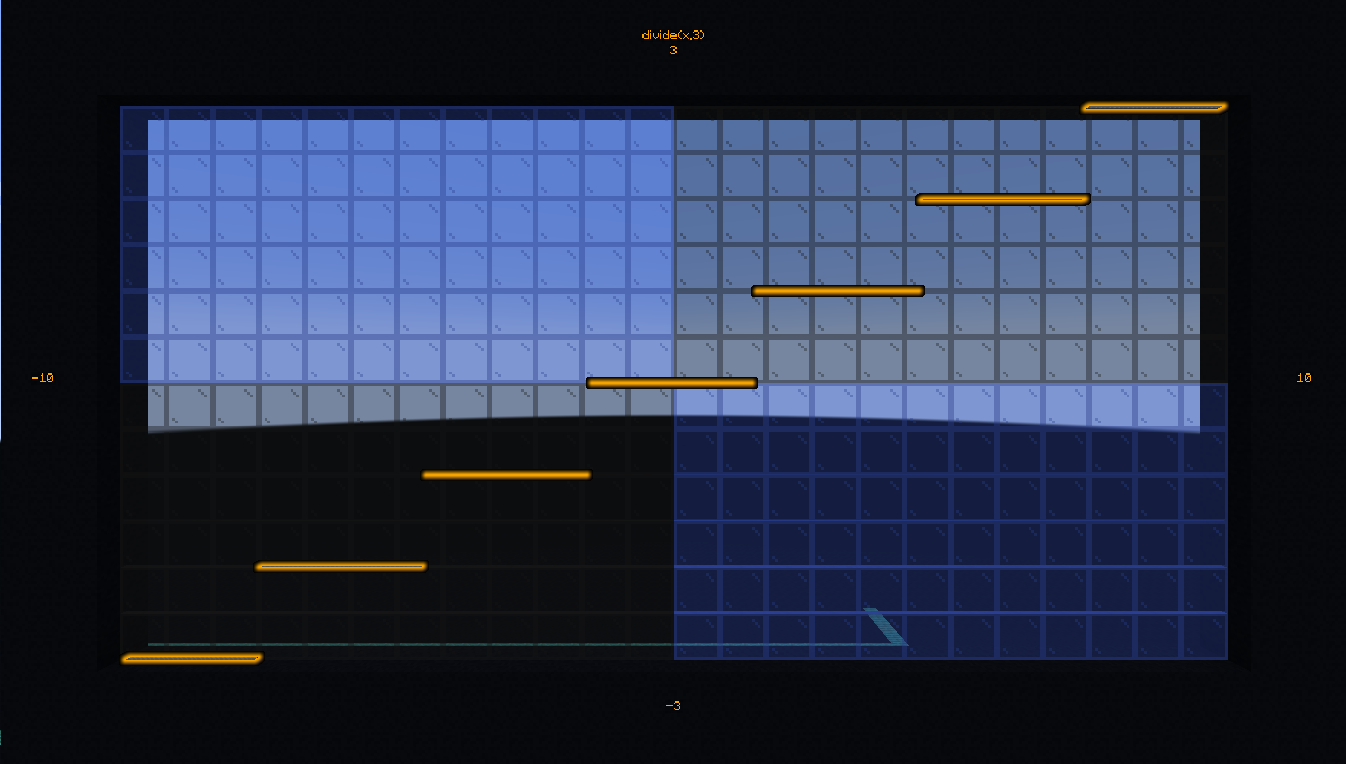
Credits: Aksiome, theogiraudet
Square root#
- #bs.math:isqrt
Compute the square root of an int number.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.isqrt.value bs.in: Number you want to calculate the square root of.- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.isqrt bs.out: Floored result of the square root.
Calculate and display \(\sqrt{42}\):
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.isqrt.value bs.in 42
function #bs.math:isqrt
tellraw @a [{"text": "sqrt(42) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.isqrt", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
- #bs.math:sqrt
Compute the square root of a floating number.
- Inputs:
Storage
bs:in math.sqrt.value[number]: Number you want to calculate the square root of.- Outputs:
Storage
bs:out math.sqrt[float]: Result of the operation.
Calculate and display \(\sqrt{42}\):
# Once
data modify storage bs:in math.sqrt.value set value 42
function #bs.math:sqrt
tellraw @a [{"text": "sqrt(42) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"nbt": "math.sqrt", "storage": "bs:out", "color": "gold"}]
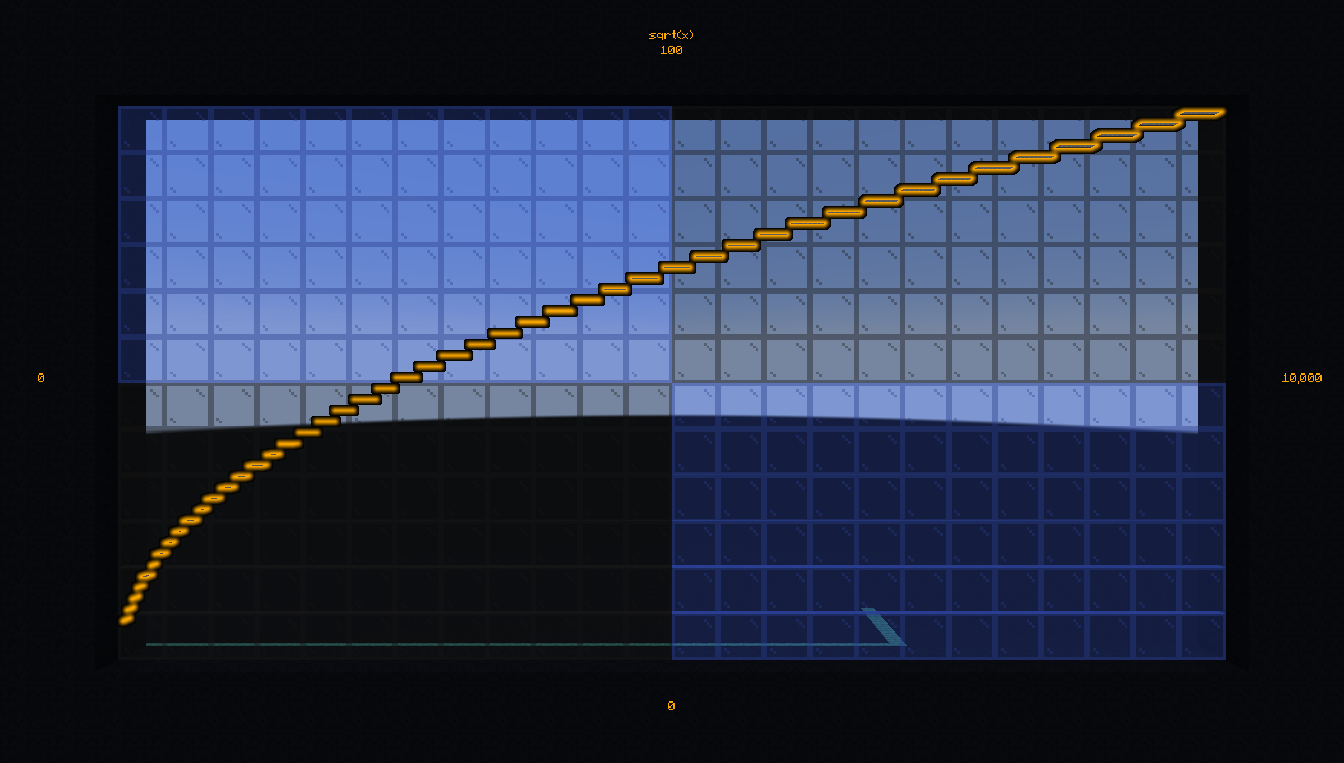
Credits: Ethanout
Trigonometry#
- #bs.math:cos
Compute the cosine of an angle between 0 and 360.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.cos.angle bs.in: Angle in degrees shifted by 2 digits (ex: 90.15 -> 9015).- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.cos bs.out: Cosine of the angle shifted by 3 digits (ex: 0.42 -> 420).
Compute and display the cosine of 42:
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.cos.angle bs.in 4200
function #bs.math:cos
tellraw @a [{"text": "cos(42) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.cos", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
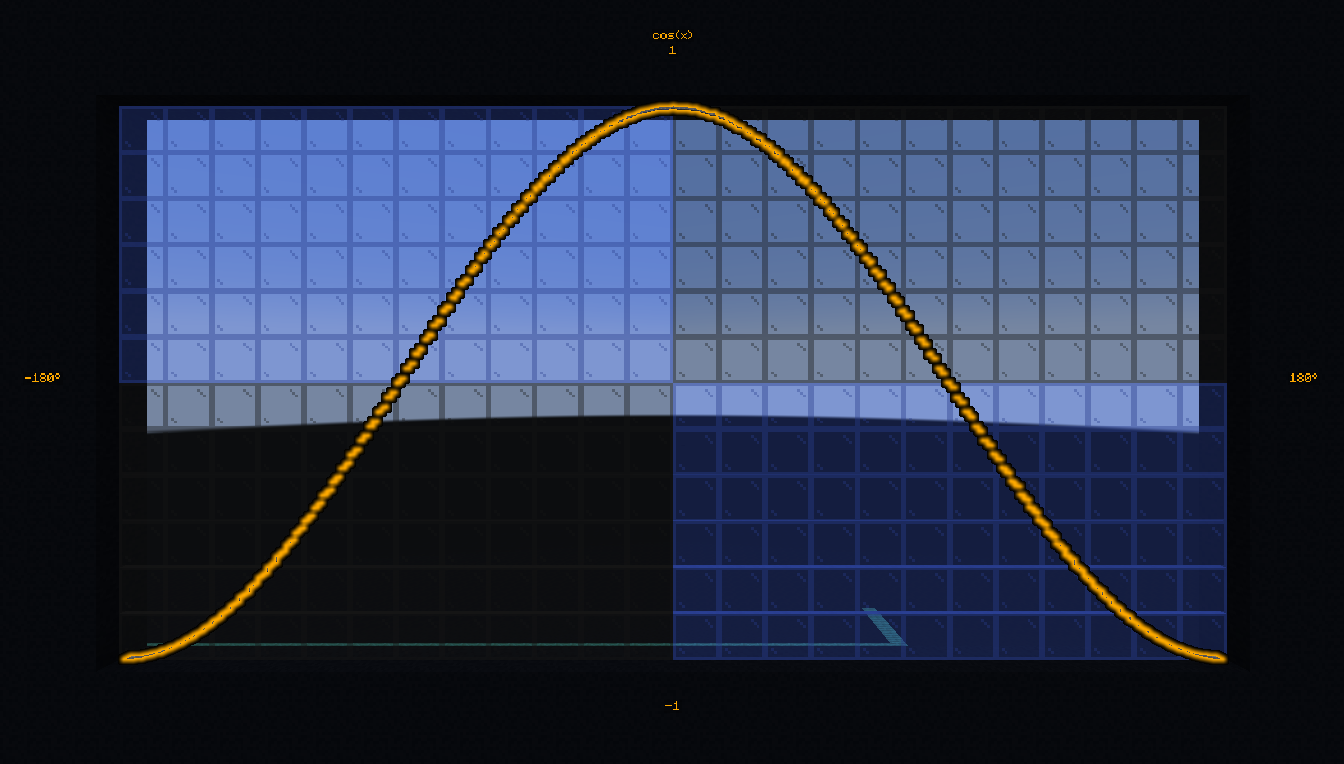
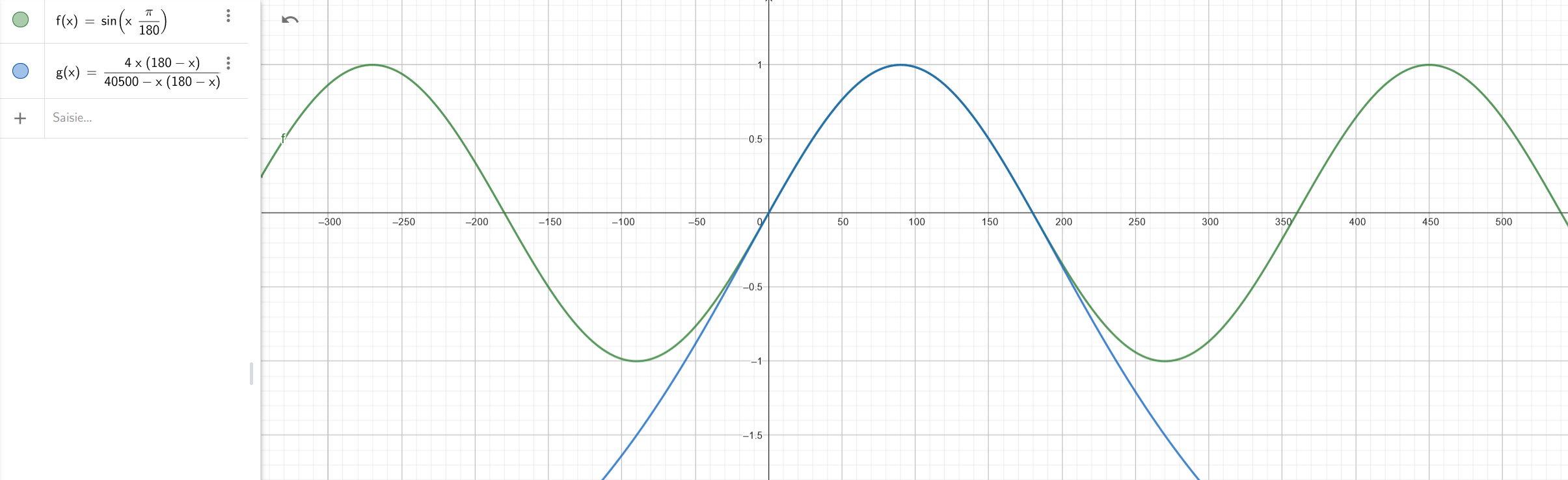
How does it work?
This functions use the Bhaskara approximation which tell us that
From this relation, and using the properties
\(\sin(-x) = -\sin(x)\) (antisymetry)
\(\sin(x+360) = \sin(x)\) (periodicity)
We can compute the sine of any angle and thus the cosine.
- #bs.math:sin
Compute the sine of an angle between 0 and 360.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.sin.angle bs.in: Angle in degrees shifted by 2 digits (ex: 90.15 -> 9015).- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.sin bs.out: Sine of the angle shifted by 3 digits (ex: 0.42 -> 420).
Compute and display the sine of 42:
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.sin.angle bs.in 4200
function #bs.math:sin
tellraw @a [{"text": "sin(42) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.sin", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
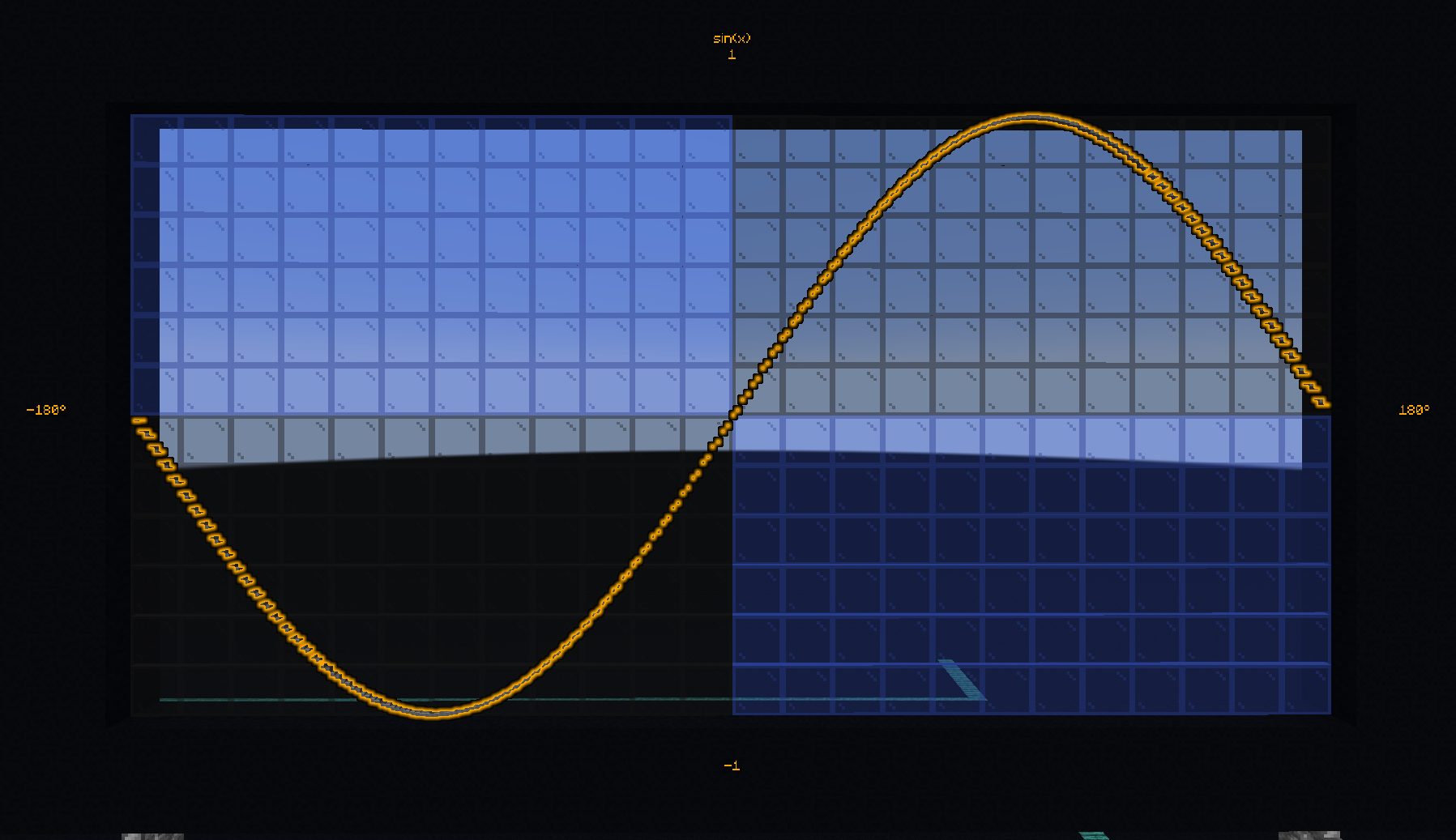
How does it work?
This functions use the Bhaskara approximation which tell us that
From this relation, and using the properties
\(\sin(-x) = -\sin(x)\) (antisymetry)
\(\sin(x+360) = \sin(x)\) (periodicity)
We can compute the sine of any angle.

- #bs.math:tan
Compute the tangent of an angle between 0 and 360.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.tan.angle bs.in: Angle in degrees shifted by 2 digits (ex: 90.15 -> 9015).- Outputs:
Return | Score
$math.tan bs.out: Tangent of the angle shifted by 3 digits (ex: 0.42 -> 420).
Compute and display the tangent of 42:
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.tan.angle bs.in 4200
function #bs.math:tan
tellraw @a [{"text": "tan(42) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.tan", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
- #bs.math:sincos
Compute both the sine and cosine of an angle between 0 and 360 in a single operation.
- Inputs:
Score
$math.sincos.angle bs.in: Angle in degrees shifted by 2 digits (ex: 90.15 -> 9015).- Outputs:
Score
$math.sincos.cos bs.out: Cosine of the angle shifted by 3 digits (ex: 0.42 -> 420).Score
$math.sincos.sin bs.out: Sine of the angle shifted by 3 digits (ex: 0.42 -> 420).
Compute and display the sine and cosine of 42:
# Once
scoreboard players set $math.sincos.angle bs.in 4200
function #bs.math:sincos
tellraw @a [{"text": "cos(42) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.sincos.cos", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
tellraw @a [{"text": "sin(42) = ", "color": "dark_gray"},{"score":{"name":"$math.sincos.sin", "objective": "bs.out"}, "color": "gold"}]
Credits: Aksiome, Leirof
💬 Did it help you?
Feel free to leave your questions and feedbacks below!